simple elements
multiple correctors
primary fertilizers
hormones
other phytoregulators
- IAA – Indole-acetic acid
- IBA – Indole-butyric acid
- NAA – Naphtaleneacetic acid

Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)
CAS No: 87-51-4
IAA is a plant hormone of wide-spectrum, belonging to the auxin family plant growth regulators. It is used as main ingredient in some commercial rooting products, in order to stimulate rooting of cuttings of herbaceous and woody crops and ornamentals.
Application Range: Rice, Peanut, Cotton, Eggplant, Peach, Plum, Apple, Pine, Grape Mulberry, Poplar, Meta sequoia, Potato, sweet potato, Kiwi, Corn, Bean, Carrot, Melon, Watermelon, Tomato.
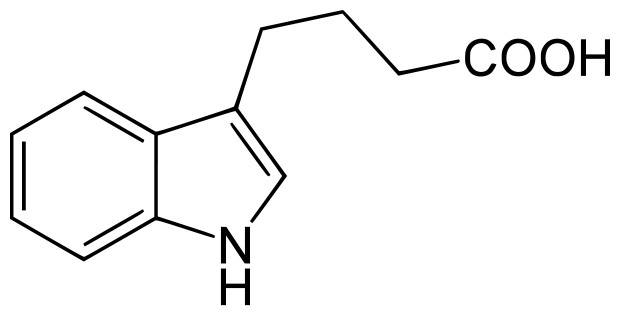
Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA)
CAS No: 133-32-4
IBA is a plant hormone of the auxin family. It is used as main ingredient in several commercial rooting compounds. It also increases fruit set of crops and is also recommended when in vitro propagation is carried out, because when combined with cytokinins like kinetin, auxins like IBA give rise to masses of undifferentiated cells called callus.
Callus formation is often used as a first step in micropropagation processes, for the callus cells are used as starting point to form other tissues.
Application Range: Cherry, Dianthus, Chrysanthemum, Jasmine, Peach, Magnolia, plum tree, Azalea, Rhododendron, Apple, Grape, Kiwi, Melon, Tea, Metasequoia, Poplar, Pine, etc.

1-Naphtaleneacetic acid (NAA)
CAS No: 86-87-3
Specification: 98% TC
Auxins induce development of phloem and xylem, also cell differentiation, as well as regeneration of the vascular tissues in plants. For this reason, it is widely used in micro propagation of crops. In cropping, auxins promote rooting, and are also required for fruit growth and development. NAA also increases fruit set and parthenocarpy in the absence of fertilization. Auxins also delay fruit senescence.
NAA is widely used in agriculture, plant nursery and forestry, to stimulate rooting in cuttings and improve setting in fruit, also to prevent pre-harvest drop. NAA is often used in order to induce flowering in some crops, such as pineapple (caused by the auxin-induced production of ethylene). NAA may also be used to prevent sprout of potato tubers.
Application Range: Wheat, Soybean, Beetroot, Tobacco, Cannabis, Cotton, Potato, Cabbage, Sugar Cane, Metasequoia, Mint, Rice, etc.
- GA3 – Gibberellic acid
- GA4 + GA7

Gibberellic acid (GA3)
CAS No: 77-06-5
Gibberellins accelerate vegetative shoot growth, producing larger plants. They also increase cell division.
Effects:
-Generally reinforce apical dominance.
-Stimulate flowering in absence of necessary exposure to cold temperatures and/or specific requirements of photo period or light intensity. For example, it has an efficient effect in solving the blooming of flowers in breeding of hybrid rice.
-Increases fruiting. It stimulates early flowering and has the property of inducing parthenocarpic fruit set in some species, such as pears.
-Breaking seed dormancy. Accelerates the germination of some seeds.
-Breaking dormancy of the vegetative organs. Induces sprouting of bulbs and tubers.
Application Range: All plants.
Alfalfa: increases the height of plants, obtaining softer stalks.
Artichoke: induces growth and earliness, and lengthens the stem.
Almond: delays flowering.
Apples ‘Golden Delicious’: prevents rust. Improves fruit setting.
Bean: increases fruit set, reduces cycle time and increases yielding.
Clementine and lemon: induces fruit set and fruit setting, avoids falling off.
Grapes: induces elongation of fruit peduncles and growing of fruits. Enhances yielding of seedless grapes.
Cotton fruiting: standardizes and reduces the losses of the first capsules.
Celery: If counteracts the problems of calcareous and saline soils, allowing early harvesting
Cucumber: encourages fruit set.
Cherry: delays the collection and staggering dates of collection, improving quality and size of the fruit, and counteracts the effects of viral diseases.
Aubergine: higher yielding.
Lettuce: improves vegetative growth and uniformity, advances harvesting, and induces seed formation.
Mango: reduces the number of flowers and increases fruits size and weight.
Melon, Cucumber and Watermelon: Increases fruit size and facilitate handling, transport and storage of fruits, during and after harvest.
Orange: improves skin toughness, prevents rind senescence, helps fruits to stay longer in the tree, thus enabling to extend marketing campaigns.
Pear: improves fruit setting, promotes formation of parthenocarpic fruits, and palliates the effects of frosts.
Pea: improves plant growth and increases yielding.
Plum: delays harvesting, reduces internal browning and increases yielding.
Seed potatoes: stimulates sprouting.
Spinach: increases fresh weight, improves appearance and enables mechanical harvesting.
Sugarcane: increases yielding
Rice: promotes the emergence of rice.
Strawberry: advances flowering, improving fruit set and fruit development and growth.
Tomato: stimulates plant growing, increases fruit size, improves the consistency of the fruit skin and increases yielding.
GA4 + GA7
CAS No GA4: 468-44-0
CAS No GA7: 510-75-8
Gibberellins accelerate vegetative shoot growth leading to larger plants. Also, cell division gets increased.
Effects:
– Generally reinforces apical dominance in the plant.
– Stimulates flowering without the necessary exposure to cold temperatures and/or specific requirements of daily lighting. For example, it has an efficient effect in solving the blooming of flowers at different times in the hybrid rice breeding.
– Increases fruiting. It stimulates early flowering and has the property of inducing parthenocarpic fruit set in some species, such as pears.
– Breaks seed dormancy. Accelerates the germination of some seeds.
– Breaks dormancy of the vegetative organs. Induces sprouting of bulbs and tubers.
Usually GA4 + GA7 is used to complement the action of Gibberellic acid (GA3). It acts as a nuance element in the parthenocarpy enforcement, because the use of GA3 alone causes unusual shapes in fruits.
- 6-BA
- Kinetin

6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA)
CAS No: 1214-39-7
The major use for cytokines derives from their ability to delay senescence and maintain greenness of leafs and plants (as an inhibitor of respirator/ kinase in plants, increase post-harvest life of green Vegetables). Also, it is used to promote seed germination and end dormant state of lateral buds, and to promote fruit formulation. They modify the action of auxins in the plant, affecting internodal length and leaf growth.
Cytokines also play an important role in nodulation of leguminous. In “in vitro” culture, the applications of cytokines induce cell division in tissue culture-in the presence of auxin-, and promote shoot initiation.
Application Range: Apple, Cherry, Grape, Lettuce, Cabbage, Celery, Rice, Rose, etc.
Effects: 6-BA is a synthetic cytokinine which elicits plant growth and development responses, improving blossom and fruit setting. It can be used to promote bud breaking in rose plants. But it is also used to boost photosynthesis, delay aging, increase percentage of fertile fruit, improve quality and increase yielding. In this sense, it is used in banana, navel orange etc.

6-Furfurylaminopurine (Kinetin)
CAS No: 525-79-1
The major use of cytokines relies on their ability to delay senescence and maintain greenness of leafs and plants. As an inhibitor of respirator/ kinase in plants, kinetin increases post-harvest life of green vegetables. It also may be used to promote seed germination and to disrupt dormant states of lateral buds, and to promote fruiting.
Cytokines modify the action of auxins in plants, affecting internodal length and leaf growth. Cytokines also play an important role in nodulation of leguminous crops. In ” in vitro” culture, application of cytokines induces cell division in tissues when applied with auxins-, and promotes shoot initiation.
Application Range: Cotton, Pear, Apple, Grape, Kola Nut, Lettuce, Potato, Pepper, Chinese Rose Flower, etc.
Uses:
-Post-harvest spraying with kinetin prolongs the storage lifetime of green vegetables such as asparagus, broccoli and celery.
-The treatment of ornamental holly with this compound enables its harvest many weeks prior to use. Kinetin is also used to disrupt dormant state in lateral buds.
- ABA – Àcid abcíssic
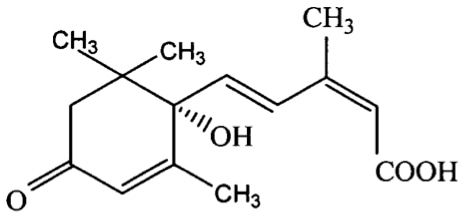
Abscisic acid (ABA, S-ABA)
CAS No: 14375-45-2
Application Range: Beans, Melons, Eggplant, Rice, Cotton, Flowers, Grass, Herbs, Fruit trees, etc.
Effects:
1) Inhibits GA, suppressing the development of lateral buds, resulting in the inhibition of branching or apical dominance.
2) Improves colouring: ABA enhances accumulation of photosynthetic compounds, increases pigment content, promotes crop ripening, keeps the bright red colour of the fruit, improves fruit quality.
3) Strengthens cereal crops, preventing them from falling down: When ABA is applied to wheat and rice, it can inhibit stem elongation, and increase the panicle weight, preventing them from falling down.
4) Helps plants to overcome environmental stress: ABA is a resistant inducing factor in plant, and it is able to activate the plant’s immune system, thus enhancing resistance in plants (cold resistance, drought resistance, antibacterial, disease resistance).
5) Promotes stomata closing: ABA can make stomata close rapidly, which has no poison on plants, becoming a safe anti transpiration agent.
6) Affects flowering: ABA can keep the terminal bud of Strawberry and Blackberry dormant, it can also promote flowering in long days.
7) Inhibits and promotes plant growing: Application of ABA through spraying at high rates can inhibit the growth of stem, hypocotyls, root, coleoptiles or leaf blade. Spraying ABA at low rates can promote rooting and strengthen hypocotyl growth, also stimulate seedlings development in fruits.
8) Keeps dormancy of bud and seeds.
mediterranea de agroquimicos
Privacy Policy
The website http://www.mediterraneadeagroquimicos.cat belongs to Mediterránea de agroquímicos, does not include cookies , and does not collect any data of visitors.





